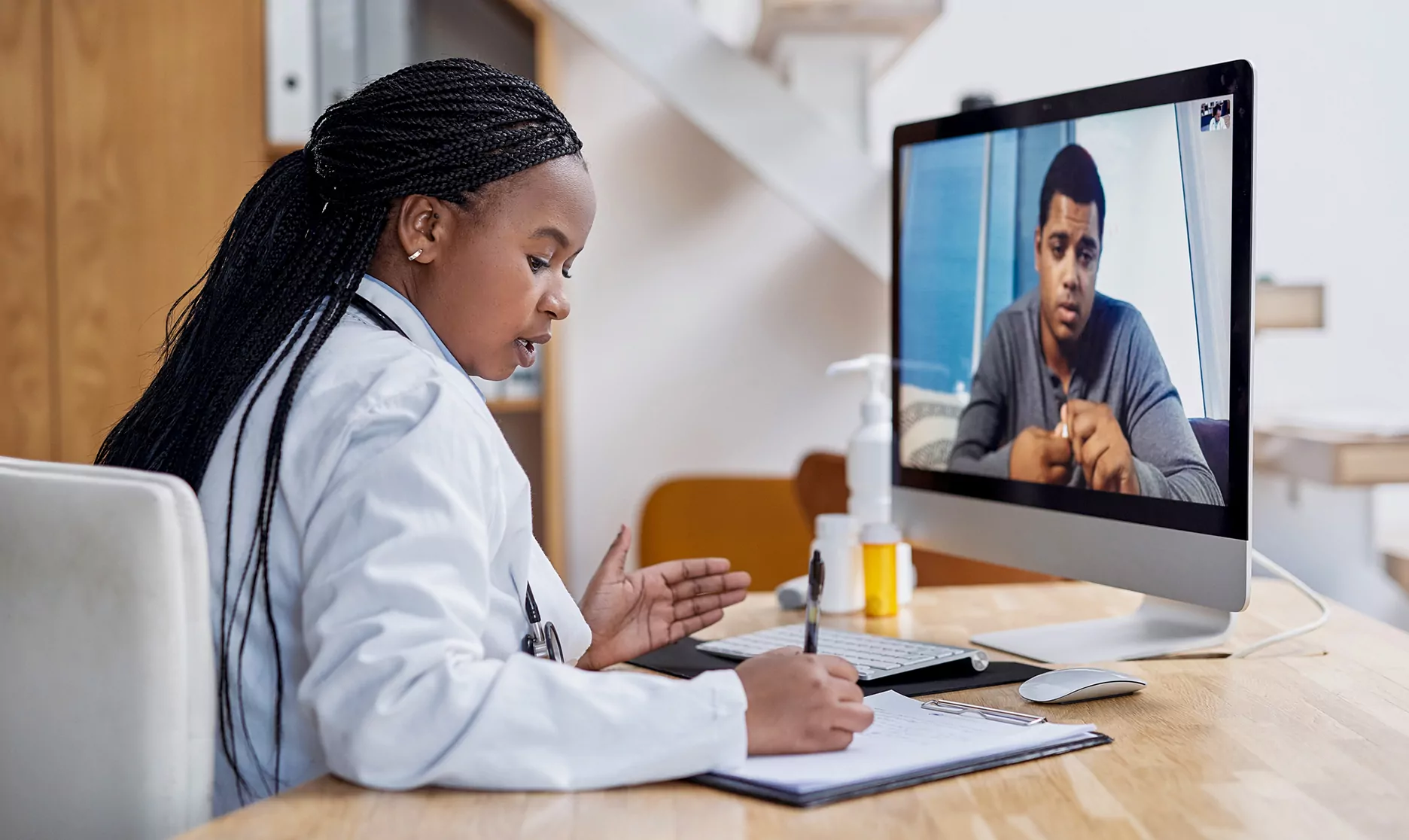
Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services remotely using telecommunications technology. It allows patients to receive medical consultation, diagnosis, and treatment without the need for physical travel, making healthcare more accessible and efficient. This technology became particularly crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic, witnessing an unprecedented increase in adoption.
The integration of telemedicine has significantly impacted the healthcare industry. It has led to the expansion of services, reaching remote and underserved areas. Telemedicine also offers a cost-effective solution for healthcare delivery, reducing the need for physical infrastructure and resources. It enhances patient engagement and satisfaction by providing convenient and immediate care.
The rise of telemedicine has attracted considerable investment, both from healthcare institutions and technology companies. Startups focusing on telehealth solutions are receiving significant funding, while established healthcare providers are investing in telemedicine platforms to expand their service offerings. The market is experiencing rapid growth, with predictions for continued expansion in the coming years.
Despite its benefits, telemedicine faces challenges. Regulatory hurdles, concerns over patient privacy and data security, and the need for technological infrastructure are key issues. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and development. There is a growing need for advanced telemedicine platforms, improved cybersecurity measures, and regulatory frameworks that support telehealth growth.
Telemedicine is expected to play a critical role in the future of healthcare. It opens up possibilities for personalized medicine, continuous patient monitoring, and integrated healthcare systems. As technology advances, telemedicine can further enhance healthcare delivery, making it more efficient, accessible, and patient-centric.








+ There are no comments
Add yours